Exploring DAG Technology: Revolutionizing Blockchain Scalability

DAG Technology: An Alternative to Blockchain
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) technology has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional distributed ledger systems in the world of cryptocurrency. This article explores the key aspects of DAG technology, its comparison with blockchain, and its potential applications.
DAG vs blockchain technology
DAG technology is often referred to as a potential disruptor due to its advantages over traditional distributed ledger systems. While blockchain remains a prominent technology in the cryptocurrency industry, DAG offers a different approach to structuring and processing transactions.
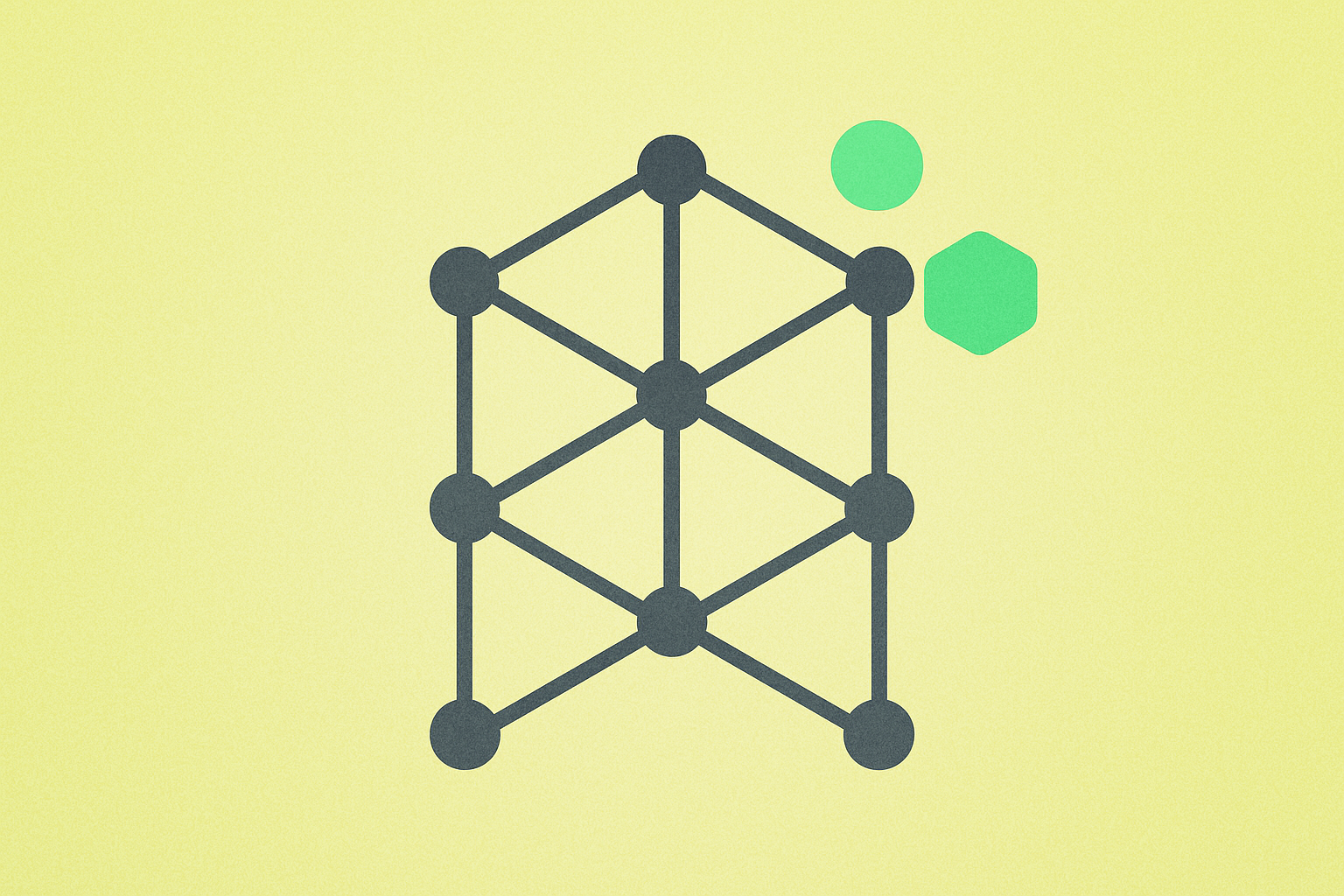
DAG architecture
The architecture of a DAG system is based on circles (vertices) and lines (edges). Each vertex represents a transaction that needs to be added to the network, while the edges indicate the order of transaction approval. This structure allows for a more efficient and scalable approach to transaction processing compared to block-based systems.
What's the difference between a DAG and a blockchain?
The main differences between DAG and blockchain technologies lie in their structure and transaction processing methods. While block-based systems create blocks of transactions, DAGs build transactions on top of one another. This fundamental difference results in faster transaction speeds and improved scalability for DAG-based systems.
How does DAG technology work?
In a DAG system, users must confirm previous transactions (called "tips") before submitting their own. This creates a layered structure of transactions, with each new transaction becoming a tip for future confirmations. The system also includes measures to prevent double-spending by assessing the entire transaction path back to the first transaction.
What is DAG used for?
DAG technology is primarily used for processing transactions more efficiently than traditional distributed ledger systems. Its key applications include:
- Fast transaction processing
- Energy-efficient operations
- Handling micropayments with low or no fees
- Improved scalability for distributed ledger systems
Which cryptocurrencies use DAG?
Several cryptocurrency projects have adopted DAG technology, including:
- IOTA (MIOTA)
- Nano
- BlockDAG
These projects leverage DAG technology to offer fast transaction speeds, scalability, security, and low or zero transaction fees.
DAG pros and cons
DAG technology offers several advantages over traditional distributed ledger systems:
- Faster transaction speeds
- Zero or low fees
- Energy efficiency
- Improved scalability
However, it also faces some challenges:
- Potential centralization issues
- Limited testing at scale
- Ongoing development and refinement needs
Conclusion
As of 2025, DAG technology continues to present an intriguing alternative to traditional distributed ledger systems, offering potential improvements in transaction speed, scalability, and energy efficiency. While it still faces challenges and is evolving, DAG has shown promise in playing a significant role in the future of distributed ledger technologies. As the technology matures and new use cases emerge, it will be interesting to see how DAG systems compare to and potentially complement existing solutions in the cryptocurrency and fintech industries.
FAQ
What is meant by directed acyclic graph?
A directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a data structure where nodes are connected by one-way links without forming cycles, used in some cryptocurrencies for faster transactions.
What is DAG used for?
DAG is used for visualizing and managing complex data workflows, representing tasks in a specific order, and optimizing processes in blockchain and cryptocurrency systems.
What is DAG with example?
DAG is a directed acyclic graph. Example: A workflow where tasks have dependencies, but no cycles exist. Nodes represent tasks, edges show dependencies.
Is DAG better than blockchain?
DAGs offer superior scalability, but blockchains have a more established track record. The choice depends on specific use case requirements.

How to Analyze NEAR Protocol's On-Chain Data: Key Metrics and Growth Trends

Exploring the Polkadot Ecosystem: A Comprehensive Guide to Blockchain Innovation

Understanding Chainlink's Role in Blockchain Architecture: Layer 1 or Not?

Understanding the Cosmos Blockchain Ecosystem

Unlocking Blockchain Interoperability with Polkadot Solutions

Guide to Engaging in Parachain Auctions on Polkadot

Fwiz (Ryan Wyatt)
What Is Holochain – Building Dapps Without Blockchain (HOT)

Latest Dropee Question of the Day and Daily Combo Answer Guide

Durable Nonce

Realized Profits and Losses
