Exploring Directed Acyclic Graph Technology in Blockchain Systems


Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) Technology: An Alternative to Traditional Distributed Ledgers
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) technology has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional distributed ledger systems in the world of cryptocurrency and decentralized networks. This article explores the key aspects of DAG technology, its comparison with other distributed ledger technologies, and its potential applications.
DAG vs traditional distributed ledger technology
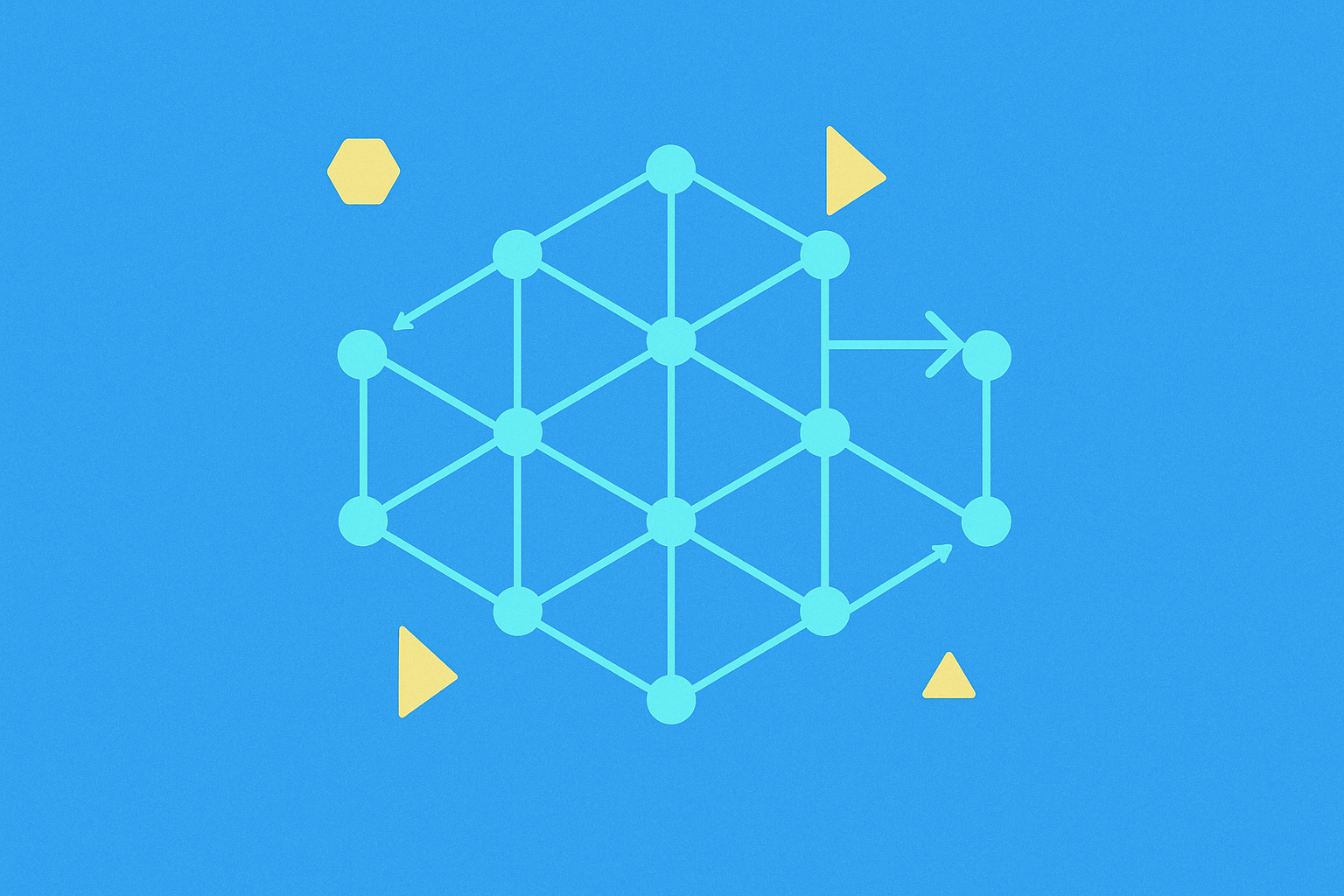
DAG technology differs from traditional distributed ledgers in several fundamental ways. Unlike systems that organize data into blocks, DAG structures transactions as interconnected nodes. This architecture allows for faster transaction processing and improved scalability. DAGs eliminate the need for block creation and mining, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower transaction fees.
How does DAG technology work?
DAG operates on a principle where each new transaction must verify two previous transactions before being added to the network. This creates a web-like structure of interconnected transactions. The system prevents double-spending by having nodes assess the entire transaction path back to the origin, ensuring the validity of each transaction. This method allows for rapid transaction confirmation and network growth.
What is DAG used for?
DAG technology finds its primary application in processing transactions more efficiently than traditional distributed ledger systems. Its key advantages include:
- Faster transaction speeds due to the absence of block creation
- Improved energy efficiency
- Suitability for micropayments due to low or zero transaction fees
- Enhanced scalability without compromising speed or efficiency
Which cryptocurrencies use DAG?
Several cryptocurrency projects have adopted DAG technology:
- IOTA (MIOTA): Known for its focus on Internet of Things applications
- Nano: Combines DAG and other distributed ledger technologies for fast, fee-less transactions
- BlockDAG: Offers energy-efficient mining through a mobile app
These projects leverage DAG's advantages to provide unique solutions in the cryptocurrency space.
DAG pros and cons
DAG technology offers several benefits but also faces some challenges:
Pros:
- Faster transaction speeds
- Zero or minimal fees
- Energy efficiency
- High scalability
Cons:
- Potential centralization issues
- Limited testing at large scales
- Ongoing development challenges
Conclusion
Directed Acyclic Graph technology presents an intriguing alternative to traditional distributed ledger systems. While it offers significant advantages in terms of speed, scalability, and energy efficiency, DAG is still evolving and being adopted. As the technology matures, it may provide innovative solutions to current limitations in distributed ledger technologies, potentially reshaping the landscape of decentralized networks in the coming years.
FAQ
What does DAG stand for?
DAG stands for Directed Acyclic Graph, a data structure used in computer science and blockchain technology for efficient data processing and consensus mechanisms.
What is a DAG slang?
DAG in slang refers to Directed Acyclic Graph, a data structure used in some cryptocurrencies for faster and more scalable transactions than traditional blockchains.
What is DAG?
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is a data structure used in blockchain technology. It allows for faster and more scalable transactions compared to traditional blockchain, as it doesn't require mining or blocks.
What does DAG mean in America?
In America, DAG stands for Directed Acyclic Graph, a data structure used in computer science and blockchain technology.

Exploring the Polkadot Ecosystem: A Comprehensive Guide to Blockchain Innovation

How to Measure Crypto Community Engagement: Key Metrics Revealed

Exploring Directed Acyclic Graphs in Blockchain Technology
Understanding Directed Acyclic Graphs in Blockchain Technology

Exploring DAG Technology in Blockchain: A New Frontier

Exploring The Benefits of DAG Technology in Blockchain Systems

Who is Vitalik Buterin? The Complete Guide to Ethereum's Founder

Which Coin Owned by Elon Musk
Hamster Kombat Daily Cipher Code Guide

Exclusive Launchpad Offer for New Users: 60% Discount on PUMP Token Subscription

P2PKH: Pay-to-PubKey-Hash in Bitcoin Transactions
