Petersen Commitment

Definition and Key Characteristics
The Pedersen Commitment is a cryptographic algorithm mainly used to enhance privacy in digital transactions and communications. It enables one party to commit to a chosen value while keeping it secret, with the option to reveal that value in the future.
As blockchain technology has advanced, the need for privacy-preserving methods has become more prominent, with the Pedersen Commitment standing out among these techniques. In cryptocurrency transactions, for example, protecting transaction amounts is critical. The Pedersen Commitment allows participants to lock in specific transaction values without immediate disclosure. This approach is essential to confidential transaction protocols in certain blockchains, strengthening both security and privacy.
Historical Context and Development
Torben Pryds Pedersen introduced the Pedersen Commitment in 1991. Since then, it has become a cornerstone in cryptographic protocol design. Originally developed to address secure information exchange, its use has grown alongside the rise of digital currencies and blockchain-based technologies. The scheme leverages homomorphic properties, enabling calculations with committed values without exposing them. This feature is especially valuable for multi-party computation and zero-knowledge proofs, which are fundamental in modern cryptography.
Applications in Modern Technology
Pedersen Commitments are widely applied in blockchain technology, particularly to enhance privacy. For example, the MimbleWimble protocol—which underpins cryptocurrencies like Grin and Beam—uses Pedersen Commitments to conceal transaction values while ensuring that no coins are illegally created or destroyed. Outside cryptocurrencies, Pedersen Commitments are also used in voting systems to guarantee that votes are cast as intended without revealing voter choices until voting concludes.
Impact on the Market and Investment Landscape
Integrating Pedersen Commitments into financial technologies profoundly influences the market, especially in trust and data security. Investors and consumers increasingly prioritize privacy and data protection, which these commitments provide. In investment environments, leveraging such cryptographic techniques attracts privacy-focused investors and can boost project valuations for those using advanced cryptography. As global data privacy regulations tighten, technologies that enable compliance through secure and private data handling—like Pedersen Commitments—are becoming even more valuable.
Emerging Trends and Future Prospects
The future of Pedersen Commitments is promising as demand for privacy and security in digital transactions rises. With ongoing advancements in quantum computing, cryptographic methods continue to evolve, and Pedersen Commitments are expected to adapt as well. Researchers are developing quantum-resistant versions, ensuring these commitments remain viable for safeguarding digital communications and transactions against future threats.
Conclusion
Pedersen Commitments are critical to modern cryptographic practice, providing privacy and security for digital transactions and communications. Their uses span blockchain technology and secure voting systems, making them indispensable across technology-driven industries. As digital privacy concerns grow, Pedersen Commitments will remain highly relevant, shaping market trends and influencing investment decisions in the tech sector.
FAQ
What is Pedersen’s Commitment Theory? What are its main principles?
Pedersen’s Commitment Theory centers on personal responsibility and life’s meaning. Its main principle is to create meaning through commitments and actions, taking responsibility for one’s own destiny.
Does Pedersen’s Commitment Theory have practical applications in law or psychology?
The theory is used in psychology to analyze human behavior and motivation. In legal practice, it helps assess parties’ good faith and responsibility in contracts and dispute resolution.
How does Pedersen’s Commitment Theory differ from other similar theories?
Pedersen’s Commitment Theory stands out for its focus on the social role and ethical impact of commitments. Unlike traditional truth theories, it looks at how commitments influence interpersonal relationships and the dynamics of trust.
How does Pedersen’s Commitment Theory influence modern society and organizational management?
Pedersen’s Commitment Theory emphasizes employee engagement and motivation, shaping modern management by prioritizing both satisfaction and productivity. It encourages a balanced approach that values both efficiency and sound decision-making.

Cryptography: From Ancient Ciphers to Blockchain. The Complete Guide to Information Security in the Digital Age
Introduction to Cryptography: A Beginner's Guide

Understanding Merkle Proofs in Blockchain Technology
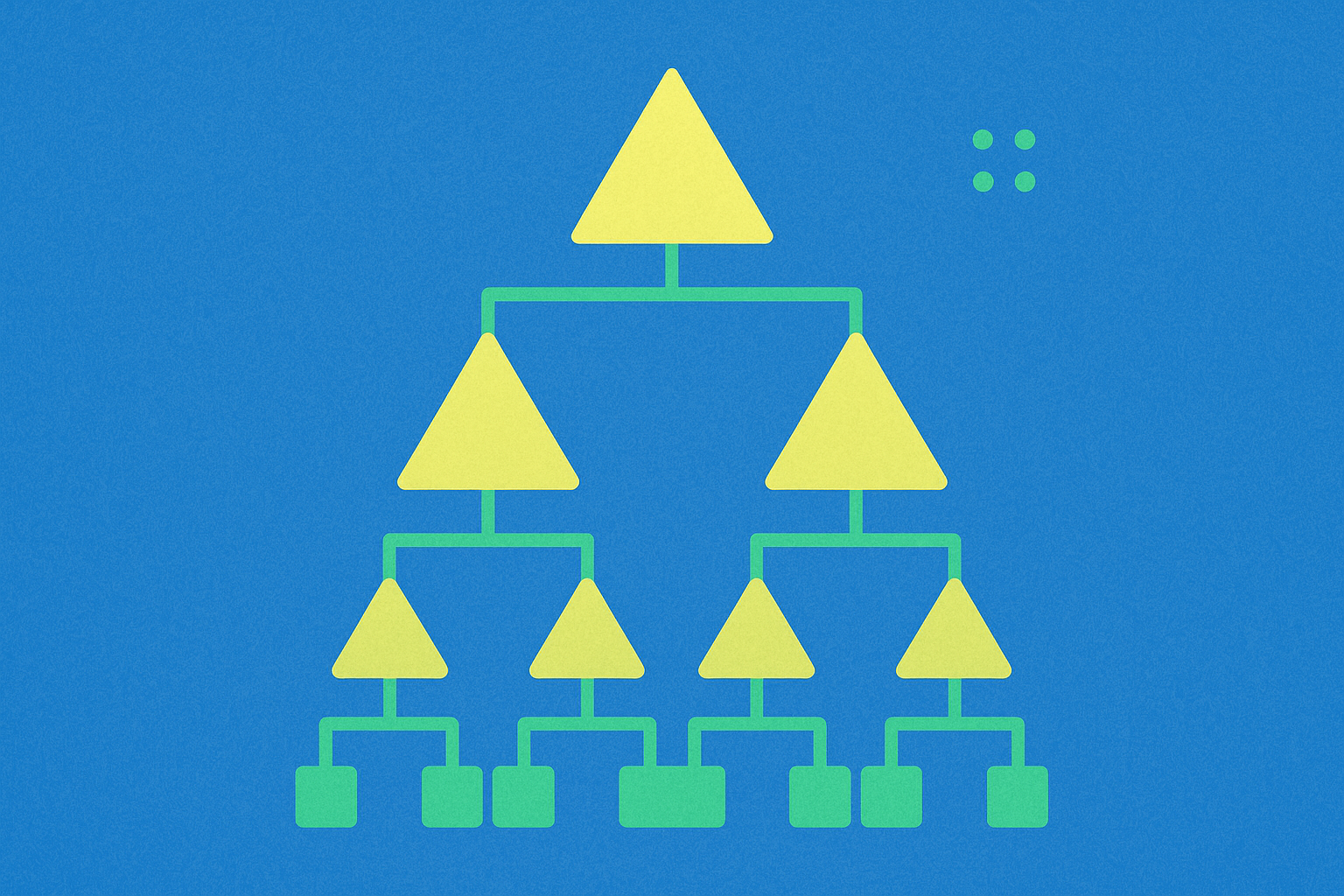

Understanding Merkle Tree Proofs in Blockchain Technology

Understanding Cryptography: Essential Concepts for Blockchain Security
Understanding Merkle Proofs in Blockchain Technology

Hamster Kombat (HMSTR) vs Dogs (DOGS): The Memecoin Battle

New Launchpad: Eigenpie, Invest BWB to Share 35,000 EGP

What Is zkSync?

Gyroscope (GYFI) Listing Launch Date & Price Forecast – Should You Buy?
Web3 Wallet vs CEX Wallet
