Trie

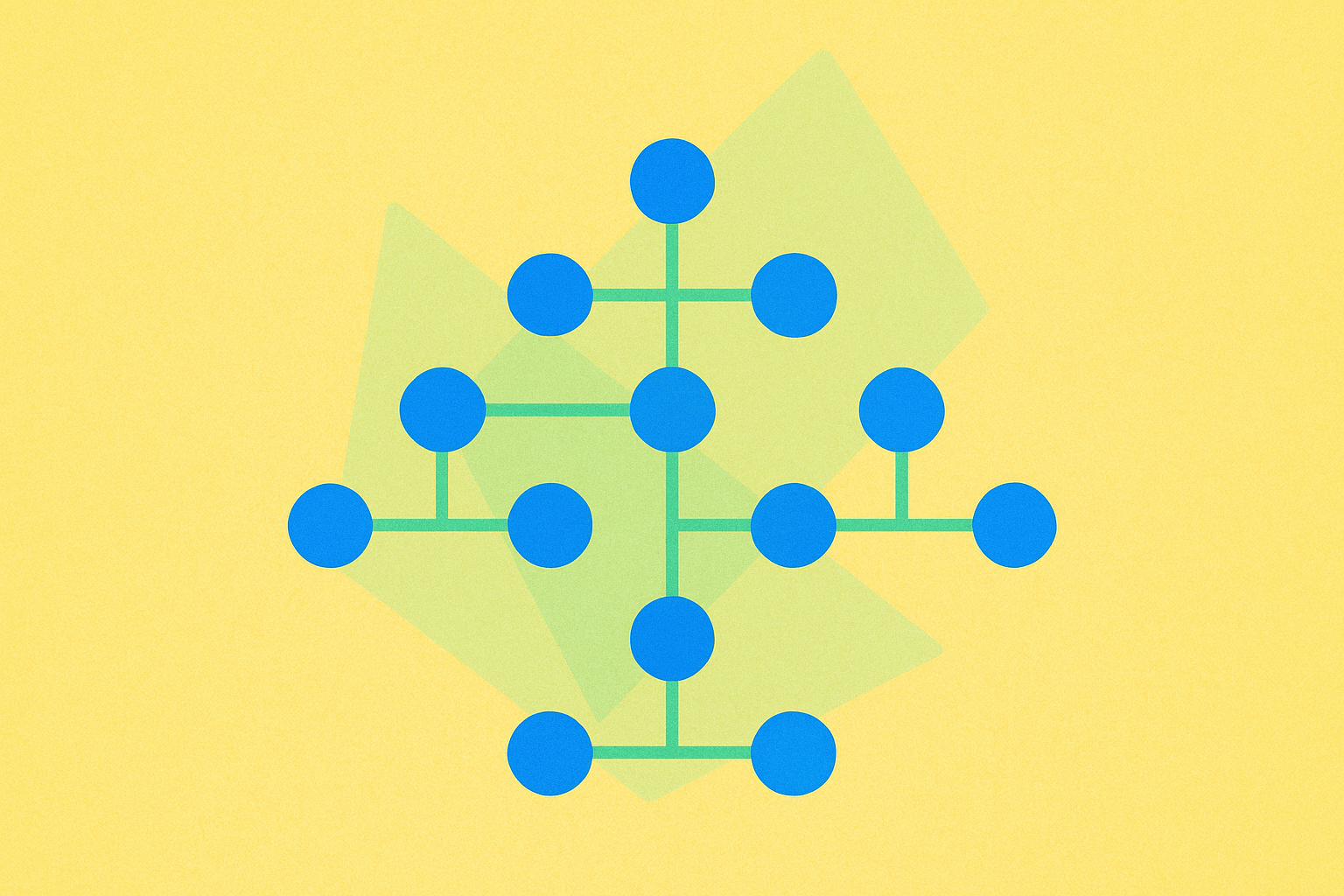
A trie, also known as a prefix tree, is a specialized type of search tree used to store dynamic sets or associative arrays where keys are typically strings. Unlike binary search trees, nodes in a trie do not store the key associated with that node directly. Instead, the position of a node within the tree structure defines its associated key, making it particularly efficient for string-based operations.
Recent advances in data retrieval and storage have highlighted the critical importance of efficient data structures like tries. For instance, Google's autocomplete feature leverages trie data structures to predict and display search queries based on the initial characters entered by users. This implementation not only enhances user experience by providing instant suggestions but also optimizes the search process by reducing the time and computational resources required to deliver relevant results. The trie's ability to share common prefixes among stored strings makes it exceptionally memory-efficient for applications dealing with large vocabularies or extensive string datasets.
Historical Context and Development
The concept of the trie was first described in a groundbreaking 1959 paper by French computer scientist René de la Briandais, who introduced the fundamental principles of this tree-based data structure. The term "trie" itself was later coined by Edward Fredkin in 1960, derived from the word "retrieval" to emphasize its primary purpose in data recovery operations. Since its inception, the trie has undergone significant evolution, driven primarily by its essential role in optimizing search queries and efficiently handling large-scale datasets.
The digital revolution and the exponential growth of data generation throughout recent decades have transformed tries from an academic curiosity into an indispensable component of modern computing infrastructure. As organizations began dealing with increasingly massive volumes of textual data, the trie's unique properties—particularly its ability to perform prefix-based searches in time proportional to the length of the search key rather than the number of keys stored—became increasingly valuable. This evolution has seen tries adapted and optimized for various specialized applications, from spell checkers and word games to database indexing and network routing protocols.
Applications in Technology
Tries are extensively employed in software development and information technology due to their unique structure and remarkable efficiency in handling complex datasets. One of their primary applications lies in autocomplete and text prediction features, which are ubiquitous in modern search engines, mobile keyboards, and text editors. These systems rely on tries to quickly traverse possible word completions based on user input, providing real-time suggestions that enhance user productivity.
Beyond text processing, tries play a crucial role in implementing IP routing algorithms, where they facilitate rapid matching of IP addresses to their corresponding networks. In network routers, tries enable efficient longest-prefix matching, which is fundamental to determining the optimal path for data packets across the internet. The structure allows routers to perform these lookups in logarithmic time relative to the address length, ensuring minimal latency in packet forwarding.
Another significant application domain is bioinformatics, where tries are utilized for efficient genome sequencing and analysis. Researchers employ trie-based algorithms to rapidly search through vast datasets of genetic information, identifying patterns, subsequences, and mutations. The ability to quickly locate specific DNA sequences within enormous genomic databases has accelerated research in personalized medicine, evolutionary biology, and disease diagnosis. Additionally, tries are employed in dictionary implementations, symbol tables, and various string matching algorithms that form the backbone of text processing systems.
Market Impact and Investment
The adoption of trie data structures by major technology companies has had a profound impact on the broader technology market and investment landscape. This widespread implementation has led to the development of faster, more efficient software solutions capable of processing massive volumes of data with greater speed and accuracy than previously possible. Such efficiency gains are particularly crucial for companies operating in the big data sector, where the ability to quickly retrieve and analyze information can provide a substantial competitive advantage in technology-dominated markets.
The economic implications of trie-based optimizations extend beyond individual companies to entire industry sectors. Organizations that successfully leverage tries in their data infrastructure often experience reduced operational costs through lower server requirements and decreased response times, leading to improved customer satisfaction and retention. These tangible benefits have attracted significant investment interest in technologies that utilize tries, particularly in artificial intelligence and machine learning platforms where efficient data structures are fundamental to algorithm performance.
Investment in trie-based technologies has grown substantially in recent years, driven by increasing demand for more sophisticated data processing capabilities. Venture capital and corporate investment have flowed into startups and established companies developing advanced search systems, natural language processing tools, and database management solutions that rely on optimized trie implementations. This investment trend reflects the recognition that efficient data structures like tries are not merely technical details but strategic assets that can determine market leadership in data-intensive industries.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of tries in technology appears exceptionally promising, with ongoing research aimed at enhancing their efficiency, scalability, and applicability to emerging computational challenges. Innovations such as compressed tries (also known as radix trees or Patricia tries) and ternary search tries exemplify how this fundamental data structure continues to evolve to meet modern computing demands. These variants reduce memory consumption while maintaining or even improving search performance, making them suitable for memory-constrained environments and embedded systems.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand and cloud computing becomes increasingly sophisticated, tries are expected to play an even more critical role in managing and querying the enormous volumes of data generated by these technologies. IoT devices produce continuous streams of time-series data, log entries, and sensor readings that require efficient indexing and retrieval mechanisms. Trie-based structures are well-suited to handle the hierarchical and prefix-based nature of many IoT data formats, from device identifiers to geographic location codes.
Emerging applications in machine learning and artificial intelligence are also driving trie innovation. Researchers are exploring how tries can accelerate neural network operations, particularly in natural language processing tasks where vocabulary management and word embedding lookups are performance bottlenecks. Additionally, the integration of tries with emerging hardware architectures, such as non-volatile memory and specialized processing units, promises to unlock new levels of performance. These developments may lead to breakthrough innovations in data handling and processing technology, potentially revolutionizing how we store, search, and analyze information across diverse application domains.
Summary
In conclusion, the trie data structure represents a powerful and versatile tool in modern computing, with widespread applications across numerous industries aimed at improving data retrieval processes and system efficiency. Its ability to efficiently process large datasets with complex string-based keys makes it indispensable in domains such as search engines, network routing, and bioinformatics. The trie's unique property of sharing common prefixes among stored keys provides both memory efficiency and fast lookup times, characteristics that are increasingly valuable as data volumes continue to grow.
As data continues to expand in both volume and complexity, the significance of tries is likely to increase correspondingly, influencing further technological development and investment in related sectors. The ongoing evolution of trie variants and optimizations demonstrates the enduring relevance of this data structure, originally conceived over six decades ago. While the specific implementation of tries on particular platforms may not always be explicitly documented, their application in improving trading algorithms, financial data processing, and real-time analytics systems is highly probable and increasingly common. The fundamental principles underlying tries—efficient prefix matching, hierarchical organization, and rapid retrieval—align perfectly with the demands of modern data-intensive applications, ensuring their continued importance in the technological landscape for years to come.
FAQ
What is Trie (Prefix Tree)? What is its basic principle?
Trie, also called prefix tree or dictionary tree, is an ordered tree structure for efficient string storage and retrieval. It shares common prefixes among strings to reduce storage space. Each node contains a character and references to child nodes, enabling fast prefix-based lookups and insertions.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Trie compared to Hash tables?
Trie offers faster query and insertion for string operations through prefix sharing, reducing character comparisons. However, it consumes more memory, especially with variable-length keys. It trades space for time efficiency.
How to implement autocomplete and search suggestions using Trie?
Trie uses a prefix tree structure to quickly match prefixes with O(m) time complexity, where m is the input string length. Store characters in nodes, mark word endings at leaf nodes, enabling fast autocomplete and search suggestions.
What are the common application scenarios for Trie in practical use?
Trie is widely used in autocomplete, spell checking and correction, sensitive word detection and filtering, prefix counting, word statistics, and efficient binary queries like maximum XOR operations.
How to implement a basic Trie data structure?
Create a node class with a hash table and a flag marking word endings. Iterate through each word and insert characters sequentially into the Trie. Share existing prefixes to optimize storage.
What are the time complexity and space complexity of Trie?
Trie has O(N) time complexity for insertion and search operations, where N is the string length. Space complexity is O(α^n), where α represents the character set size.
Blockchain Made Easy: A Beginner’s Guide to How It Works

Exploring Careers in Blockchain Development for Core Developers

Kickstart Your Career in Blockchain Development

Exploring a Career as a Blockchain Developer: Skills and Opportunities
Blockchain Basics: How It Works

Empowering India's Web3 Future: Community and Educational Initiatives

How do derivatives market signals predict crypto price volatility in 2026

What is causing GALA price volatility and can it recover in 2026
What are the key derivatives market signals for crypto trading: futures open interest, funding rates, and liquidation data explained

What are the security risks and vulnerabilities in NXPC smart contracts and cryptocurrency exchanges?

What is Ponke (PONKE): Whitepaper Logic, Use Cases, and Roadmap Analysis with $37M Market Cap
